Look, processing thousands of tax documents manually during filing season can take months and cost your organization hundreds of thousands in IRS penalties for simple data entry errors. Most finance teams spend weeks extracting data from 1099s and W-9 forms, only to find accuracy issues that trigger costly compliance problems. Modern tax document processors can cut this timeline from months to days while achieving near-perfect accuracy. Let's break down how to implement automated tax document processing that handles 1099s and W-9 forms with the precision compliance demands.
TLDR:
- Tax document processing errors result in IRS penalties of $60-$330 per form, with potential losses reaching millions annually.
- Modern AI-powered solutions like Extend achieve 99%+ accuracy vs 70-80% with traditional OCR, reducing setup from months to minutes
- Effective processing requires a contextual understanding of form relationships and advanced text extraction
- Extend's system handles W-9s and 1099s with built-in validation, human review workflows, and continuous learning
- Organizations can deploy production-ready tax automation in days while maintaining compliance standards
What's Required for Effective Tax Document Processing
Effective tax document processing demands several critical features that traditional OCR solutions often can't deliver.
Our evaluation tools help teams measure and improve accuracy across these different requirements, making sure systems meet the standards that tax compliance demands.
| Processing Requirement | Traditional OCR | LLM-Powered Solutions |
|---|---|---|
| Format Flexibility | Limited | Extensive |
| Contextual Understanding | Minimal | Advanced |
| Accuracy Rate | 70-80% | 99%+ |
| Setup Time | Months | Days |
| Maintenance Overhead | High | Low |
Build from Scratch vs Using Extend
Building tax document processing from scratch requires months of development across multiple complex components. Organizations must develop OCR engines, train machine learning models on tax forms, create validation rules, build review interfaces, and maintain accuracy over time.
This integration of cutting-edge technologies such as OCR, supervised machine learning, and automated analytics requires substantial time and technical expertise. That's assuming you have the ML expertise in-house. Most in-house projects struggle to achieve the accuracy levels needed for tax compliance, often plateauing around 80% accuracy due to the complexity of handling form variations and edge cases.
Extend is the complete document processing toolkit comprised of the most accurate parsing, extraction, and splitting APIs to ship your hardest use cases in minutes, not months. Extend's suite of models, infrastructure, and tooling give you the most powerful custom document solution, without any of the overhead. Agents automate the entire lifecycle of document processing, allowing your engineering teams to process your most complex documents and optimize performance at scale.
Our platform provides a complete tax document processing solution that achieves production-ready accuracy in days rather than months. And our LLM-powered document understanding handles complex tax forms with over 99% accuracy out of the box.
Pre-built processors for extraction, classification, and splitting remove development overhead. Human-in-the-loop workflows allow continuous improvement as the system learns from corrections.
Teams can focus on their core business rather than building and maintaining document processing infrastructure.
1. Configure Document Ingestion and Parsing
Begin by setting up Extend’s ingestion pipeline to accept PDFs, images, and scanned documents through API endpoints or batch uploads. The system is designed to handle diverse tax document formats, such as scanned W-9s, PDF 1099s from payroll providers, and mobile-captured paper forms, all funneled through a unified workflow.
Extend’s parsing engine automatically converts ingested documents into structured formats suitable for downstream processing, preserving table structures and layout context. It also handles variations in document orientation, image quality, and multi-page forms without manual pre-processing.
For platforms that support it, you can also export to structured markdown or JSON, making integration with your automation pipelines much easier.
This parsing step is essential for tax documents, as field positions can vary across form editions and different vendor software outputs. The ingestion pipeline uses AI to normalize these differences, yielding a consistent data structure regardless of document source. You’ll configure endpoints for each expected source and set up quality controls to flag exceptions requiring human review.
For more details on setting up document ingestion, check out our detailed document processing guide. You can also refer to this Quick Start (5 minutes) guide to get started.
2. Set Up Form Classification and Routing
Configure Extend's classification processor to automatically identify different tax form types such as 1099-NEC, 1099-MISC, W-9, and their different revisions. Set up routing rules that direct each form type to the appropriate extraction workflows.
Tax form classification is more complex than it appears. A 1099-NEC and 1099-MISC look similar but have different field meanings and validation requirements. The system needs to distinguish between these forms and route them to the correct processing logic.
The classification processor learns to recognize form headers, layout patterns, and key identifiers that distinguish form types. It handles changes in formatting across different tax years and software vendors.
Set up routing rules that send each classified form to its appropriate extraction workflow. W-9 forms might route to contractor onboarding processes, while 1099-NEC forms flow to payment reconciliation workflows.
Our splitter processor can also handle multi-page submissions where contractors submit multiple forms together, automatically separating and routing each document type.
Classification accuracy directly impacts downstream processing quality, so spend time configuring confidence thresholds and reviewing workflows for uncertain classifications.
3. Build Custom Extraction Schemas
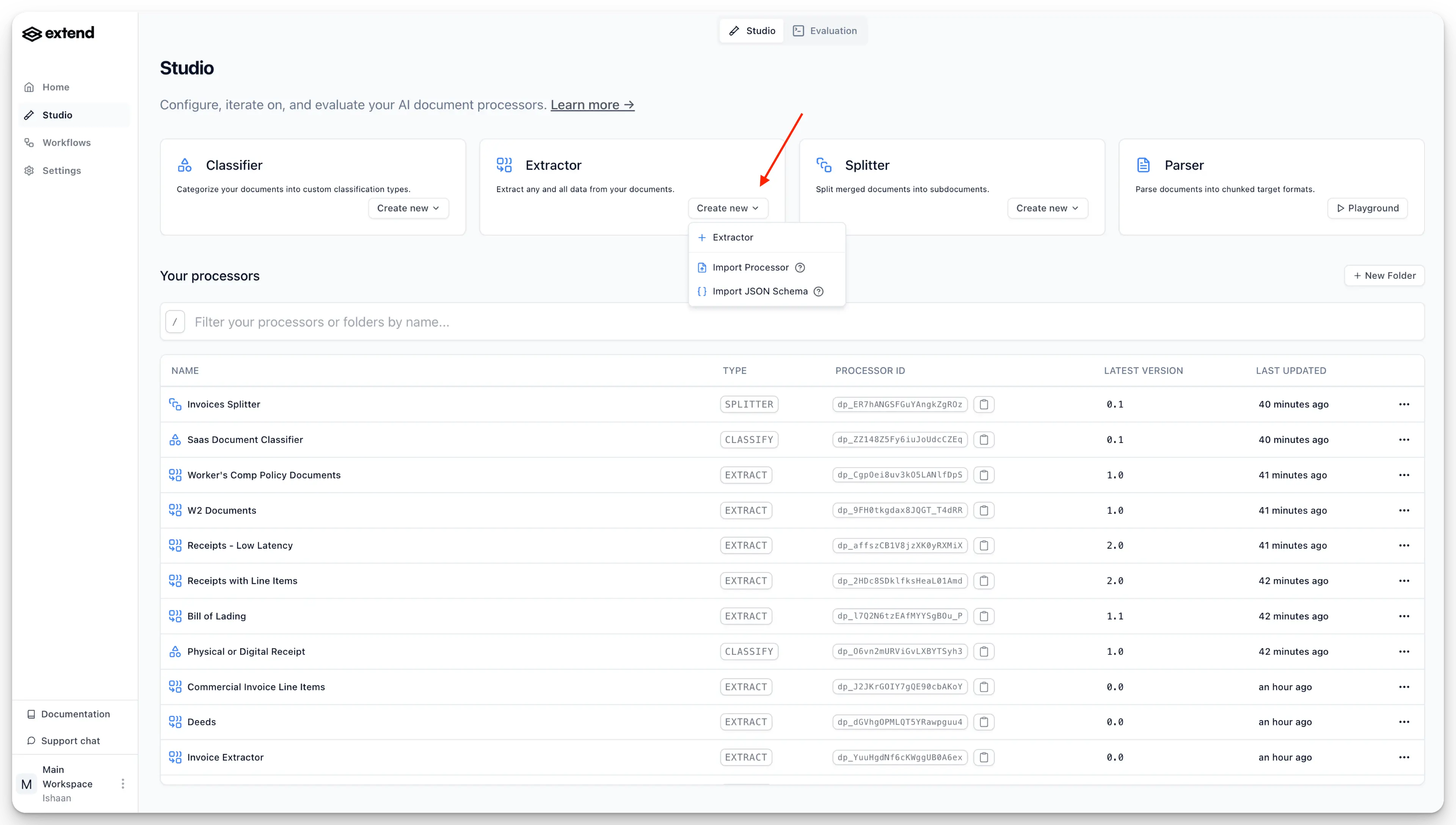
Create extraction schemas for each tax form type using Extend's configuration tools. Upload a document and watch our config gen auto generate a schema automatically.
Each tax form has dozens of potential fields, but most organizations usually only need to extract 10-15 important data points.
For W-9 forms, this typically includes name, business name, TIN, location, and entity classification. For 1099s, focus on payer information, recipient details, and payment amounts in the relevant boxes.
Set up validation rules to ensure extracted data meets IRS formatting requirements. TINs must follow specific patterns (XXX-XX-XXXX for SSNs, XX-XXXXXXX for EINs), and payment amounts need proper decimal formatting.
Configure confidence thresholds to flag uncertain extractions for human review. Tax data accuracy is important, so err on the side of caution with confidence scoring.
The schema configuration process is designed for non-technical team members. Tax professionals can define extraction requirements without writing code, making it easy to adjust schemas as requirements evolve.
We've seen teams like Nudge Security reduce their development time from months to weeks by using these pre-built configuration tools.
4. Implement Validation and Quality Controls
Set up Extend's validation features to verify extracted data quality. Configure business rules to check TIN formats, validate payment amount consistency, and flag potential errors.
Tax document validation goes beyond format checking. The system needs to verify that extracted TINs match valid patterns, that payment amounts are reasonable for the form type, and that required fields are populated.
Implement cross-form validation for related documents. When processing both W-9 and 1099 forms for the same contractor, verify that TINs and entity names match across documents. Discrepancies often indicate data entry errors or form mix-ups.
Set up confidence scoring to identify low-quality extractions. Documents with poor scan quality, unusual formatting, or handwritten entries should trigger additional review workflows.
Also, configure validation rules specific to your business requirements. If you only work with contractors above certain payment thresholds, flag 1099s with unusually low amounts for review.
These validations help prevent compliance issues before they reach downstream systems. It's much easier to catch and correct errors during processing than to find them during an IRS audit.
Teams like AbstractOps have used these validation features to dramatically improve their data quality and customer satisfaction.
5. Configure Human Review Workflows
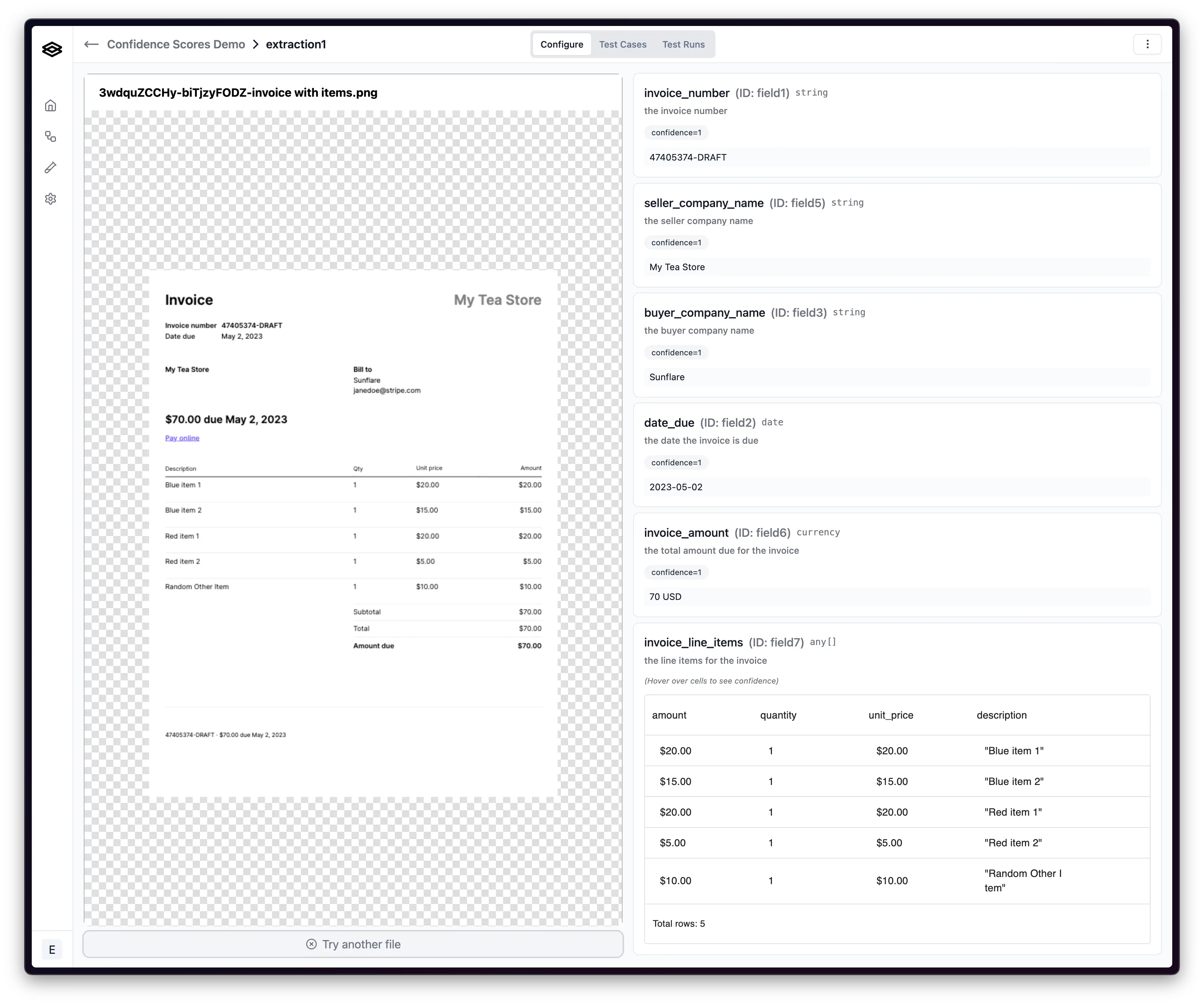
Set up human-in-the-loop workflows for cases that require manual review. Create review interfaces that allow tax professionals to verify extracted data, make corrections, and approve documents for processing.
Even with 99%+ accuracy, some documents will require human oversight. Handwritten forms, damaged scans, or unusual form variations might need expert review to maintain compliance.
When a reviewer corrects a TIN extraction, that feedback trains the system to handle similar cases better in the future.
Set appropriate routing rules so edge cases reach the right reviewers. Complex business entity classifications might need senior tax professionals, while simple data corrections can be handled by junior staff.
The review interface should present extracted data alongside the original document, making it easy for reviewers to spot and correct errors. Include confidence scores and validation flags to help reviewers focus on the most uncertain extractions.
Track review metrics to identify patterns in errors and improvement opportunities. If certain form types consistently require review, that indicates opportunities for schema or validation refinements.
Companies like HomeLight have achieved 99% accuracy by implementing effective human review workflows that continuously improve system performance.
6. Set Up Output Integration and Delivery
Configure Extend's output features to deliver processed data to downstream systems. Set up API integrations to push extracted data to tax software, ERP systems, or databases.
Tax document data needs to flow into multiple systems: accounting software for expense tracking, tax preparation tools for compliance filing, and ERP systems for contractor management. Each system may require different data formats and field mappings.
Configure batch exports for bulk processing scenarios. During tax season, you might process thousands of forms daily and need efficient bulk delivery to downstream systems.
Make sure proper formatting works for downstream consumption. Some tax software expects specific field names or data formats, so configure output mappings accordingly.
Set up error handling for integration failures. If a downstream system is unavailable, queue the data for retry rather than losing processed information.
Speaking of which, consider implementing webhook notifications to alert downstream systems when new tax documents are processed. This allows real-time integration workflows that keep all systems synchronized.
Teams like Vendr have used these integration features to unlock new product features and business opportunities from their document processing workflows.
7. Deploy and Monitor Performance
Launch your tax document processing workflow and set up ongoing monitoring. Use Extend's analytics suite to track accuracy metrics, processing volumes, and error rates.
Set up dashboards to monitor key performance indicators, such as processing throughput, accuracy rates by form type, review queue lengths, and integration success rates. These metrics help identify bottlenecks and improvement opportunities.
Configure alerts for unusual patterns or quality issues. A sudden drop in accuracy might indicate changes in document sources or new form variations that need attention.
Review performance regularly and make adjustments to improve accuracy and throughput as document volumes change. Tax season brings volume spikes that might require workflow adjustments or additional review capacity.
Track the business impact of your automation. Measure time savings, error reduction, and compliance improvements to show ROI and support continued investment in the system.
Plan for seasonal variations in document processing. Tax document volumes fluctuate dramatically throughout the year, so make sure your monitoring and alerting can handle these patterns.
As your system processes more documents and receives more feedback, accuracy will continue improving. Through this continuous improvement process, we've seen organizations achieve near-perfect accuracy on their specific document types.
FAQs
1. How long does it take to set up automated tax document processing?
Most teams can get a prototype processing pipeline running in hours and achieve production-grade accuracy in days with Extend rather than the traditional months-long timeline required for building from scratch.
2. What accuracy rates can I expect for 1099 and W-9 form processing?
Extend consistently achieves over 99% extraction accuracy on tax documents, compared to 70-80% accuracy with traditional OCR solutions. This helps organizations avoid costly IRS penalties from data entry errors.
3. Can the system handle different formats and quality levels of tax documents?
Yes, Extend processes virtually any document format, from pristine PDFs to degraded scans and mobile photos. It maintains high accuracy even on poor-quality documents through advanced LLM-powered document understanding. Built-in agentic OCR helps to parse degraded documents by using a VLM to review and make edits to low confidence OCR errors.
4. What happens when Extend encounters uncertain extractions?
The system includes built-in confidence scoring and human-in-the-loop workflows that flag uncertain extractions for expert review, and the system learns from these corrections to improve future accuracy on similar documents.
5. How does automated processing help with IRS compliance requirements?
The system includes strong validation rules that verify TIN formats, cross-form data consistency, and payment amount accuracy, helping prevent the $60-$330 per form penalties from processing errors.
Final thoughts on automated tax document processing
The difference between manual tax processing and AI-powered automation is measured in months, not days. Organizations that adopt modern document processing solutions eliminate costly penalties while freeing their teams to focus on strategic work rather than data entry. The technology exists today to change your tax workflows from a compliance burden into a competitive advantage.
