Most of your organization’s knowledge doesn’t live in rows and columns, it’s buried inside contracts, emails, PDFs, and scanned images that traditional systems can’t parse or analyze. This unstructured data accounts for roughly 70–80% of enterprise data, leaving critical insights locked away from analytics and automation. Fortunately, intelligent document processing solutions are closing this gap by transforming messy, unstructured files into structured, searchable data that teams can actually use.
TL;DR:
- Unstructured data makes up the majority of all organizational data but resists traditional database storage
- AI-powered processing achieves 99%+ accuracy vs 80% with legacy OCR on complex documents
- Modern LLMs require semantic chunking and context engineering to process documents effectively
- Organizations reduce document processing time with automated unstructured data solutions
- LLM-powered pipelines can convert complex, unstructured documents into structured data within days
Understanding Unstructured Data
Unstructured data is information that doesn't follow conventional data models, making it difficult to store and manage in mainstream relational databases. Unlike structured data that fits neatly into rows and columns, unstructured data exists in its native format without predefined organization.
Think of emails, PDFs, images, videos, social media posts, and audio files. These formats don't conform to traditional database schemas, yet they contain valuable information that businesses desperately need to extract and analyze.
The scale is staggering. Unstructured information accounts for 70-80% of all data in organizations today. This explosion creates both opportunity and challenge. While unstructured data holds insights that can change business operations, traditional tools struggle to process it effectively.
Types and Examples of Unstructured Data
Text-Based Unstructured Data
Text-based includes PDFs, email messages, PowerPoint presentations, survey responses, call center transcripts, and social media posts. These are the most common unstructured data sources in business environments.
Consider the daily influx: customer support tickets, contract negotiations via email, meeting notes, and regulatory filings. Each contains critical business intelligence but lacks the standardized format needed for traditional analysis.
Legal documents show this challenge clearly. A single contract might contain payment terms, liability clauses, and termination conditions scattered across dozens of pages without consistent formatting.
Multimedia Content
Rich media files like audio and video don't fit into structured data models. Images from quality control processes, training videos, and customer testimonials contain valuable insights trapped in formats that resist conventional analysis.
Medical imaging, security footage, and product photography generate terabytes of visual data daily. Without AI-powered processing, this information remains largely untapped.
Machine-Generated Data
IoT device sensors generate extraordinarily large volumes of unstructured log files. Server logs, network traffic data, and application performance metrics flood systems with business intelligence.
Machine-generated data often contains the most actionable insights but requires specialized processing to unlock its value.
Manufacturing sensors, GPS tracking, and system monitoring tools produce continuous streams of unstructured data that traditional databases struggle to accommodate effectively.
For document-heavy industries, solutions like tax document processing show how AI changes unstructured forms into structured, actionable data.
Structured vs Unstructured vs Semi-Structured Data
Understanding the three data types requires looking at how information is organized and stored. Each serves different business needs and requires distinct processing approaches.
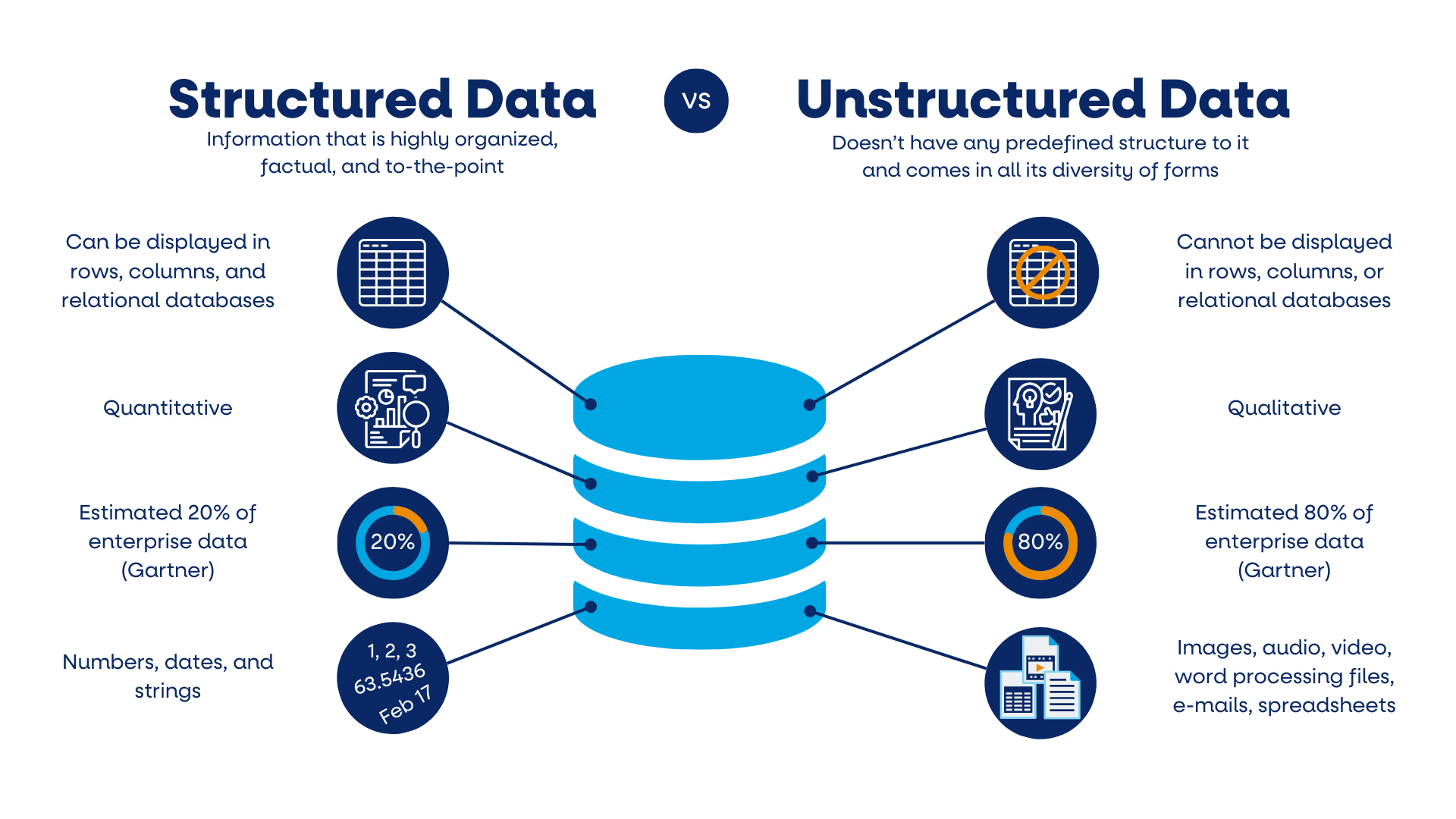
- Structured data follows rigid schemas with predefined relationships. Database tables, spreadsheets, and CRM records show this format. Every field has a specific data type, length, and validation rule.
- Unstructured data lacks any organizational framework. Documents, images, and videos contain valuable information but resist traditional database storage. This format dominates business communications and content creation.
- Semi-structured data bridges both worlds. JSON uses hierarchical structures with key-value pairs, making it readable for humans and machines. XML uses tags to define elements and attributes, commonly found in web services and configuration files.
Semi-structured data serves as the bridge between rigid database schemas and completely unorganized content. It uses metadata like tags and semantic markers to identify specific characteristics without requiring predefined models.
Semi-structured formats like JSON and XML provide flexibility while maintaining some organizational structure, making them ideal for APIs and data exchange.
For logistics companies processing bills of lading, the challenge involves converting unstructured shipping documents into structured data that systems can process automatically.
Unstructured Data in AI and LLM Applications
Data Preparation for LLMs
Segmentation of content into semantic chunks provides meaningful input for LLMs. This process breaks documents into logical sections while preserving context, so models receive coherent information instead of arbitrary text fragments.
LLMs have limitations on input and output text volume they can handle effectively. Smart chunking strategies respect these constraints while maintaining document coherence and meaning across segments.
Quality preprocessing directly impacts model performance. Clean, well-structured inputs produce more accurate outputs, while poorly prepared data leads to hallucinations and unreliable results.
RAG Systems and Document Processing
RAG architectures depend entirely on high-quality unstructured data processing. These systems retrieve relevant document segments to augment LLM responses with current, domain-specific information that wasn't present during training.
By comprehending context and semantics of text, LLMs can fix problems after OCR engines initially recognize text. This greatly increases accuracy, particularly in complicated or noisy images.
Modern AI systems treat unstructured data as the primary source of business intelligence, requiring sophisticated preprocessing to unlock its full potential.
Document processing becomes the foundation for reliable AI applications. Companies using document processing software benefit from purpose-built pipelines that change complex documents into LLM-ready formats, allowing accurate extraction and analysis at scale.
Business Applications and Use Cases
Industry-Specific Applications
Healthcare organizations use unstructured data to change patient care and improve daily operations. Medical imaging analysis allows faster diagnosis, while processing clinical notes and research papers speeds up drug discovery and treatment protocols.
Financial services firms extract insights from loan applications, regulatory filings, and market research reports. AI-driven voice analytics improves customer service while monitoring compliance across thousands of recorded interactions daily.
Retail organizations analyze customer reviews, social media sentiment, and product feedback to drive merchandising decisions and improve customer experience strategies.
Workflow Improvements
Processing unstructured data eliminates manual data entry bottlenecks that plague document-heavy workflows. Teams redirect hours from repetitive tasks toward strategic analysis and decision-making activities.
How Extend Changes Unstructured Data Processing
Extend is the complete document processing toolkit comprised of the most accurate parsing, extraction, and splitting APIs to ship your hardest use cases in minutes, not months. Extend's suite of models, infrastructure, and tooling is the most powerful custom document solution, without any of the overhead. Agents automate the entire lifecycle of document processing, allowing your engineering teams to process your most complex documents and optimize performance at scale
Extend's AI-first architecture shows a fundamental shift from legacy OCR approaches. Built from the ground up with LLMs and VLMs, the system handles complex documents far beyond traditional tools, maintaining exceptional accuracy even on degraded scans.
Traditional OCR tools struggle with tables, handwriting, and varied layouts. Extend's models expertly parse these challenging elements while preserving spatial relationships and document context that simpler systems lose.
The system processes any document format while maintaining layout integrity. This feature changes messy PDFs, scanned forms, and even photos of paper documents into clean, structured outputs ready for downstream AI processing.
End-to-End Processing Pipeline
Extend's automated workflows chain multiple processors into custom pipelines tailored to specific use cases. Teams can configure classification, extraction, splitting, and validation steps that execute automatically without manual intervention.
The system uses semantic chunking to break documents into logical sections without losing context. This gives downstream models well-structured inputs instead of arbitrary text fragments that confuse analysis.
Pre-built processors for common tasks can deliver very high accuracy (often 99%+) out-of-the-box on well-optimized document types, whereas legacy workflows often show significantly higher error rates.
Extend's continuously improving pipelines learn from each correction to adapt to your organization's specific documents over time.
Teams deploy production-ready solutions in days instead of the months required for traditional integrations. The developer-friendly API allows smooth embedding into existing products and internal systems, delivering results in seconds for real-time user experiences.
Human-in-the-loop review tools maintain oversight for critical workflows while capturing feedback that teaches the AI to handle edge cases more effectively with each iteration.
FAQs
How do you process unstructured data for AI applications?
Modern AI processing uses semantic chunking to break documents into logical sections while preserving context, then applies LLM-powered models to extract and structure the information. This approach achieves over 99% accuracy compared to 80% with traditional OCR methods.
Can unstructured data be converted into formats that existing business systems can use?
Yes, AI-powered systems like Extend can change unstructured documents into structured formats like JSON or database-ready outputs that integrate smoothly with existing business systems, allowing automated workflows and real-time processing.
What types of documents work best with modern unstructured data processing?
Complex documents with tables, handwriting, varied layouts, and poor scan quality that traditionally challenge OCR systems work exceptionally well with LLM-powered processing, including invoices, contracts, medical records, shipping documents, and regulatory forms.
Final thoughts on managing unstructured data effectively
The rise of unstructured data marks a turning point for how organizations manage knowledge and make decisions. Static files and legacy systems can’t keep up with the scale, speed, or complexity of modern information flows, but AI-powered document intelligence changes that. By converting contracts, forms, and images into structured, system-ready data, Extend enables teams to unlock insights that were previously inaccessible. The organizations adopting this approach today aren’t just keeping pace with data growth, they’re building the infrastructure for faster, smarter operations tomorrow.
